
1. Giải bất phương trình \(\dfrac{{x + 2}}{{3x + 1}} > \dfrac{{x – 2}}{{2x – 1}}\) .
2. Xác định m để hệ bất phương trình sau có nghiệm duy nhất
\(\left\{ \begin{array}{l}2x + 1 – m \le 0\\mx + 2x – 1 \le 0\end{array} \right.\)
1.
Ta có
\(\begin{array}{l}\dfrac{{x + 2}}{{3x + 1}} > \dfrac{{x – 2}}{{2x – 1}}\\ \Leftrightarrow \dfrac{{x + 2}}{{3x + 1}} – \dfrac{{x – 2}}{{2x – 1}} > 0\\ \Leftrightarrow \dfrac{{\left( {x + 2} \right)\left( {2x – 1} \right) – \left( {x – 2} \right)\left( {3x + 1} \right)}}{{\left( {3x + 1} \right)\left( {2x – 1} \right)}} > 0\end{array}\)
Advertisements (Quảng cáo)
\(\begin{array}{l} \Leftrightarrow \dfrac{{ – {x^2} + 8x}}{{\left( {3x + 1} \right)\left( {2x – 1} \right)}} > 0\\ \Leftrightarrow \dfrac{{x\left( { – x + 8} \right)}}{{\left( {3x + 1} \right)\left( {2x – 1} \right)}} > 0\end{array}\)
Bảng xét dấu
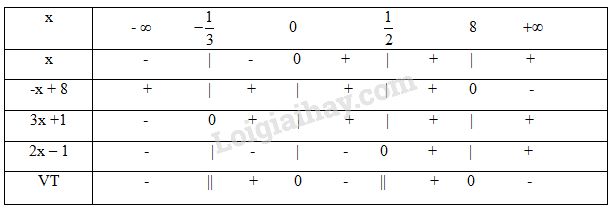
Bất phương trình có tập nghiệm \(S = \left( { – \dfrac{1}{3};0} \right) \cup \left( {\dfrac{1}{2};8} \right)\) .
Advertisements (Quảng cáo)
2.
Ta có \(\left\{ \begin{array}{l}2x + 1 – m \le 0\\mx + 2x – 1 \le 0\end{array} \right.\\ \Leftrightarrow \left\{ \begin{array}{l}x \le \dfrac{{m – 1}}{2}{\rm{ (1)}}\\\left( {m + 2} \right)x \le 1{\rm{ (2)}}\end{array} \right.\)
Xét bất phương trình (2) . có ba trương hợp
+) \(m = -2\): (2) trở thành \(0x \le 1\) .Bất phương trình có nghiệm là mọi \(x \in \mathbb{R}\) . Suy ra hệ có vô số nghiệm.
+) \(m > -2\): (2) có nghiệm \(x \le \dfrac{1}{{m + 2}}\) . Suy ra hệ có vô số nghiệm.
+) \(m < -2\): (2) có nghiệm \(x \ge \dfrac{1}{{m + 2}}\). Suy ra hệ có nghiệm duy nhất khi và chỉ khi \(\begin{array}{l}\dfrac{{m – 1}}{2} = \dfrac{1}{{m + 2}} \Leftrightarrow {m^2} + m – 2 = 2\\ \Leftrightarrow {m^2} + m – 4 = 0\\ \Leftrightarrow m = \dfrac{{ – 1 \pm \sqrt {17} }}{2}\end{array}\)
Kết hợp với điều kiện \(m < -2\) chọn \(m = \dfrac{{ – 1 – \sqrt {17} }}{2}\) .

