Câu 1: Làm tính nhân
a.\(3x\left( {5{x^2} – 2x – 1} \right)\)
b. \(\left( {{x^2} + 2xy – 3} \right)\left( { – xy} \right)\)
c. \({1 \over 2}{x^2}y\left( {2{x^3} – {2 \over 5}x{y^2} – 1} \right)\)
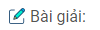
a. \(3x\left( {5{x^2} – 2x – 1} \right) = 15{x^3} – 6{x^2} – 3x\)
b. \(\left( {{x^2} + 2xy – 3} \right)\left( { – xy} \right) = – {x^3}y – 2{x^2}{y^2} + 3xy\)
c. \({1 \over 2}{x^2}y\left( {2{x^3} – {2 \over 5}x{y^2} – 1} \right) = {x^5}y – {1 \over 5}{x^3}{y^3} – {1 \over 2}{x^2}y\)
Câu 2: Rút gọn các biểu thức sau
a. \(x\left( {2{x^2} – 3} \right) – {x^2}\left( {5x + 1} \right) + {x^2}\)
b. \(3x\left( {x – 2} \right) – 5x\left( {1 – x} \right) – 8\left( {{x^2} – 3} \right)\)
c. \({1 \over 2}{x^2}\left( {6x – 3} \right) – x\left( {{x^2} + {1 \over 2}} \right) + {1 \over 2}\left( {x + 4} \right)\)
Advertisements (Quảng cáo)
a. \(x\left( {2{x^2} – 3} \right) – {x^2}\left( {5x + 1} \right) + {x^2}\)=\(2{x^3} – 3x – 5{x^3} – {x^2} + {x^2} = – 3x – 3{x^3}\)
b. \(3x\left( {x – 2} \right) – 5x\left( {1 – x} \right) – 8\left( {{x^2} – 3} \right)\)
\( = 3{x^2} – 6x – 5x + 5{x^2} – 8{x^2} + 24 = – 11x + 24\)
c. \({1 \over 2}{x^2}\left( {6x – 3} \right) – x\left( {{x^2} + {1 \over 2}} \right) + {1 \over 2}\left( {x + 4} \right)\)
\( = 3{x^3} – {3 \over 2}x – {x^3} – {1 \over 2}x + {1 \over 2}x + 2 = 2{x^3} – {3 \over 2}x + 2\)
Câu 3: Tính giá trị của các biểu thức sau
a. P= \(5x\left( {{x^2} – 3} \right) + {x^2}\left( {7 – 5x} \right) – 7{x^2}\)
Advertisements (Quảng cáo)
b. Q= \(x\left( {x – y} \right) + y\left( {x – y} \right)\)
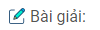
Trước hết ta rút gọn biểu thức.
a.P=\(5x\left( {{x^2} – 3} \right) + {x^2}\left( {7 – 5x} \right) – 7{x^2}\)
= \(5{x^3} – 15x + 7{x^2} – 5{x^3} – 7{x^2} = – 15x\)
Thay \(x = – 5\) vào P \( = – 15x\) ta có: P=−15.(−5)=75
b.\(x\left( {x – y} \right) + y\left( {x – y} \right)\)=\({x^2} – xy + xy – {y^2} = {x^2} – {y^2}\)
Thay \(x = 1,5;y = 10\) vào Q\( = {x^2} – {y^2}\) ta có:
Q= \({\left( {1,5} \right)^2} – {10^2} = – 97,75\)
Câu 4: Chứng tỏ rằng giá trị của các biểu thức sau không phụ thuộc vào giá trị của biến
a. \(x\left( {5x – 3} \right) – {x^2}\left( {x – 1} \right) + x\left( {{x^2} – 6x} \right) – 10 + 3x\)
b. \(x\left( {{x^2} + x + 1} \right) – {x^2}\left( {x + 1} \right) – x + 5\)
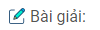
a. \(x\left( {5x – 3} \right) – {x^2}\left( {x – 1} \right) + x\left( {{x^2} – 6x} \right) – 10 + 3x\)
\( = 5{x^2} – 3x – {x^3} + {x^2} + {x^3} – 6{x^2} – 10 + 3x = – 10\)
Vậy biểu thức không phụ thuộc vào \(x\)
b. \(x\left( {{x^2} + x + 1} \right) – {x^2}\left( {x + 1} \right) – x + 5\)
\( = {x^3} + {x^2} + x – {x^3} – {x^2} – x + 5 = 5\)
Vậy biểu thức không phụ thuộc vào \(x\)

